ELCB AND RCCB (RCD)
Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker (ELCB)
Working Principle of ELCB
An Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker (ELCB) is
a security device used in an electrical installation to detect leakage current
and protect humans against the risk of an electric shock, from this leakage
current. The operation is such that, the power supply connected at its
switching terminal (contact of the circuit breaker) is disconnected by a special type of latching
relay when it detects a leakage current. Thereby, protecting individuals getting
in contact with this leakage current against the risk of an electric shock. This circuit
breaker remains OFF until reset manually.
Types of Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker
They
are two types of Earth Leakage Circuit Breakers. They are named based on their
principle of operation. They are;
- The Voltage Earth Leakage Device (Known as the ELCB) and
- The Current Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker (RCD or RCCB).
In
the past, when referring to Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker (ELCB), this referred
to both the voltage operated Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker
(ELCB) and the differential current operated Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker (ELCB).
This brought confusion in the electrical technology industry.
In order to curb this confusion, the International Electrotechnical commission (IEC) adopted to term the current operated Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker, the Residual Current Device (RCD) or Residual Current Circuit Breaker (RCCB).
In order to curb this confusion, the International Electrotechnical commission (IEC) adopted to term the current operated Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker, the Residual Current Device (RCD) or Residual Current Circuit Breaker (RCCB).
An
ELCB has a test button (T) which can be used to test if the circuit breaker
functions normally.
Note:
It is essential to note that this circuit breaker is mainly used in the TT
system and it is very essential to choose the correct type in an electrical
installation for maximum protection.
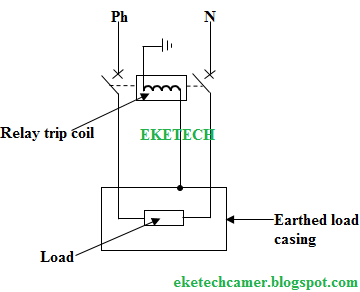
Voltage Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker (ELCB)
As
the name indicates, this ELCB is voltage operated. This ELCB has a relay coil
with one terminal connected to the ground, and the other terminal connected to
the metallic body part of equipment(s). The earth wire can be seen in the figure below.
Circuit (schematic) diagram of a voltage operated earth leakage circuit breaker (ELCB)
Operating principle of a voltage ELCB (ELCB)
When
a live wire accidentally touches the metallic body part of the equipment in
question or the metallic part becomes live by some other means, a voltage is
setup across the sense coil and if the voltage is significant, the relay coil
of the circuit breaker is energized and switches its contact thereby disconnecting
the power supply.
Characteristics of ELCB
Some
of the characteristics of an ELCB include:
- The phase, neutral and earth wire
are connected to the circuit breaker
- Operating time of ELCB: 0.1s
- It is used in high Earth impedance earthing system to avoid shock.
Disadvantages of ELCB
- If the earth wires is not connected to the ELCB, it won’t be able to trip. If the equipment’s body part is not connected to the earth terminal of the ELCB, it won’t be able to detect the earth leakage fault.
- · Nuisance tripping: this can occur during lightning strike which can create a potential in the soil thereby presentng a sufficient voltage at the sense coil which causes the ELCB to trip. This same phenomenon can also be caused when two earth rods are closer and a high earth leakage current from one, can creat a potential between the two causing it to trip.
Current Earth Leakage Circuit
Breaker (Current-ELCB)
or Residual Current Device (RCD) or Residual Current Circuit Breaker (RCCB)
The
functioning of this circuit breaker is completely different to that of an ELCB.
As the name suggest, this device is current operated. The operating principle
is such that, the circuit breaker has a current transformer which is energized
from the phase and neutral to open its contacts from the relay coil in case of
an earth leakage fault.
Schematic diagram of an RCCB (RCD)
Circuit
diagram of an RCCB (RCD)
Operating principle of an RCCB (RCD)
In
order to balance the current, the phase (live) and neutral wires are wound
round the soft iron core in opposite direction.
In
normal conditions, the same amount of current entering the phase (Ip) returns
through the neutral wire (In). Hence, the net magnetomotive force in the core is
zero, and no flux is linked in the detector coil.
Ip=In
and Il= Ip- In =0
In the case of an earth leakage fault, the
amount of current entering the phase (Ip) is not equal to that leaving through
the neutral wire (Ip) due to the leakage current (Il).
Hence, there will be a net magnetomotive force in the core which induces a flux in the detector coil (current transformer). This then energizes the relay or trip coil and its contacts opens thereby putting OFF the power supply.
Hence, there will be a net magnetomotive force in the core which induces a flux in the detector coil (current transformer). This then energizes the relay or trip coil and its contacts opens thereby putting OFF the power supply.
Ip ≠ In and Il=
Ip - In ≠0
An RCB can detect an
earth leakage in an equipment (just by monitoring the live and neutral) even if
the equipment is not earthed. This property have made the RCD more popular.
Characteristics of RCCB
Some
of the characteristics of an RCCB are:
- The phase and neutral are connected
to the circuit breaker and the amount of current entering the phase should
return through neutral.
- Rated current 16A to 125A
- Sensitivity ranges 10mA, 30mA,
100mA, 300mA, 500mA, and 1000mA
- Trip time: 30 milliseconds.
Limitations of an RCD (RCCB)
- Nuisance tripping: this circuit breaker due to its high sensitivity, may often trip on sudden change in load due to a brief small leakage current. This mostly occur in old appliances.
- ELCBs are less sensitive to fault conditions than RCDs, and therefore have fewer nuisance trips.
- An RCCB does not protects against short circuit, overload and heating. Such conditions might instead damage the RCD.
- Touching the live and neutral at the same time, you would receive an electric shock because the current is balanced (the current entering the phase is equal to that leaving the neutral). So for protection against short circuit, an MCB can used.
RCBO
There
now exist combined RCCB and MCB in a single structure or unit called an RCBO
(Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Over current Protection) which offers
protection against earth leakage, short circuit and overload.
by EKETECH