GENERATION OF ELECTRICAL ENERGY FROM BIOMASS
1.1.
INTRODUCTION
Energy is the most vital issue for all living-being on
earth. Modern life style has further increased its importance since a faster
life means a faster transport, faster communication, faster manufacturing
processes etc. All these lead to an increase in energy required for all these
modern systems. These energy come from different sources and one of these
sources is the biomass or biofuel energy production (generation)
source.
1.2.
DEFINITION OF BIOMASS
Biomass
or Biofuel is a fuel that is developed
from organic materials, renewable and sustainable source of energy used to generate electricity or other forms of energy. It is the organic material that is
used for the production of energy known as biomass.
1.3.
DESCRIPTION
The biomass plant is a renewable source of energy
because wastes residues will always exist be it in terms of scrap wood, forest
resources, manure etc...Developing new energy sources to produce reliable,
affordable energy while respecting the environment is one of the top most
compelling need of this system.
Most bio-power plants function when wastes is burned
and the energy in it released as heat(steam) runs a turbine to make or to generate
electricity and also provides heat to industries and home. Biomass is burned
directly to produce high pressure steam (heat) that drives a turbine generator
to generate or make electricity. In some biomass industries, the extracted or
spent steam is used for manufacturing processes or to heat buildings.
In the case of CAMEROON being a developing country,
biomass or biofuel is mostly used for domestic purposes such as cooking,
smoking, roasting, drying crops etc... For the moment, biofuel is the main source
of energy. This is mostly in the form of firewood, charcoal, dung etc. some of
the biofuel is used at the industrial level. For example the Cameroon
Development Cooperation uses biomass (palm husks and rubber wood) in its oil
mills and Tole tea factory. While it is used in the tea factory mostly as a
source of direct heat for drying tea leaves, in the oil mill it is used as a
direct source of heat for boiling kenels and also, by converting the heat into
mechanical energy for the production of electricity.
A simple biomass system shown in the figure below is
made up of several key components. For a steam cycle, this includes:
- Fuel storage and handling equipment.
- Combustor/ furnace.
- Boiler,
pumps, fans.
- Steam turbine.
- Generator, condenser.
- Cooling tower, exhaust/ emission control etc.
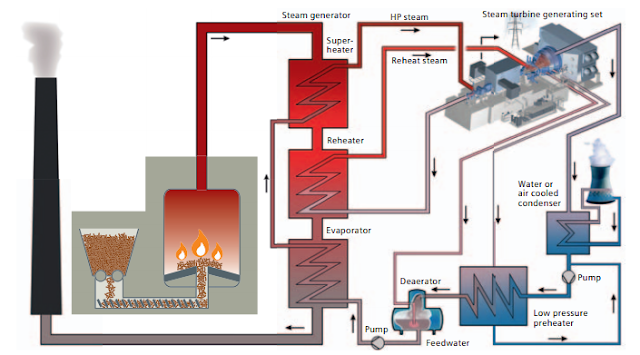 |
| A general view of a biomass power plant system |
1.1.1. METHODS
TO CONVERT BIOMASS TO ELECTRICITY
The figure below shows the general methods and process
in the production of energy from biomass.
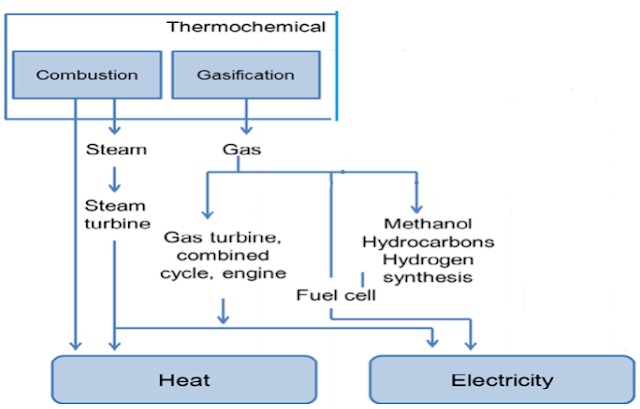 |
Different methods and processes for energy production
from biomass.
A) COMBUSTION
Burn the biomass directly which produces heat.
The heat production by recovering heat through heat transfer media such as
steam and hot water using boilers and heat exchangers is send to the steam turbine which then generates
electricity. Combustion can be represented by:
C6H10O5 +6O2---------->6 CO2 + 5 H2O + 17.5 MJ / Kg.
C6H10O5 +6O2---------->6 CO2 + 5 H2O + 17.5 MJ / Kg.
Biomass
+ Oxygen (air) Carbon dioxide + water +
heat.
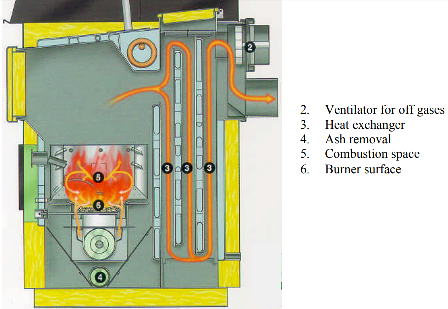 |
| Combustion process for energy production |
A) GASIFICATION
This is the process of converting
biomass solid raw material (e.g. wood) into fuel gas or chemical feedstock gas
(syngas).This
gasification is also subdivided into other types.
a)
A
biomass gasifier takes dry biomass such as agriculture waste and with the
absence of oxygen and high temperature produces synthesis gas (CO+H2); also
known as pyrolysis of biomass.
b)
Gasification
also takes wet biomass such as food waste and manure into methane (CH4) in a
digestion tank. Both methane and synthesis gas (syn gas) can be used in a gas
engine or a gas turbine for energy production.
c)
Another
way to produce electricity from gasification is by using fuel cells. If we have
enough purity, we can use fuel cells to produce electricity. The fuel cells
break quickly if the gas in any way contains impurities but this technology is
not yet commercial.
d)
Biofuel
like ethanol, biodiesel and bio-oil can also be used for power production in
most types of power generation plants.
The general process of gassification is shown in the
figure below.
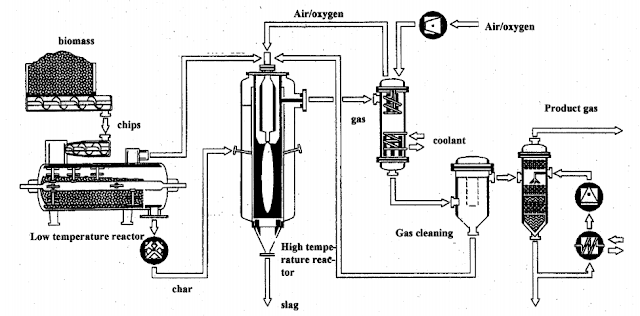 |
Overview of gasification process in energy production
|
1.1. PROCEDURES NECESSARY BEFORE BIOMASS IS INSTALLED
This type of a system is best suitable for a
particular application and which depends on many factors including:
-
Availability
and cost of each type of biomass (chip, pellets, house waste, forest residues
etc.).
-
Competing
fuel cost (fuel oil and natural gas).
-
Peak
and annual electricity load and cost.
-
Building
size and type.
-
Space
availability.
-
Operation
and maintenance staff availability.
-
Local
emission regulation.
1.2. ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF A BIOMASS SYSTEM
1.2.1. MERITS
-
It
has an advantage of dispatchability meaning it is controllable and available
when needed.
-
The
waste material reduces landfilled disposal and makes more space for everything
else.
-
Carbon
dioxide which is released when biomass fuel is burnt is taken in by plants.
-
Less
money is spent for oil.
1.2.2. DEMERITS
-
The
fuel needs to be procured, delivered, stored and paid for.
-
Also,
biomass combustion produces emissions which must be carefully monitored and
controlled to comply with regulation.
-
Additional
work is needed in areas such as harvesting methods because land used for energy
crops may be in demand for other purposes such as farming, conservation,
housing etc.
-
Some
biomass conversion projects are from animal wastes and are relatively small and
therefore limited.
-
In
some cases, it is a major cause of pollution.
-
Research
is needed to reduce the cost of production for biomass based fuel.
-
Agricultural
wastes will not be available if the basic crop is no longer grown.
1.3.
CONCLUSION
Biomass system ranges from small stoves used in homes
for heating or cooking to large power plant used by centralized utilities to
produce electricity. In residential areas, biomass can be used for space
heating or for cooking. Here, wood is the common source of fuel, although many different
materials are used. In industrial and business, biomass is used for several
purposes including space heating, hot water heating, and electricity generation
which is the main proponent for this topic.
By EKETECH