GCE Advanced Level Past Questions
Technical and Vocational Education Examinations
Electrical Power Systems EPS
Power Electronics
|
Specialty
Name (Specialty Code) |
Electrical Power Systems
EPS (F3) |
|
Subject
Title |
Power Electronics |
|
Paper
Nº |
2 |
|
Subject
Code Nº |
7235 |
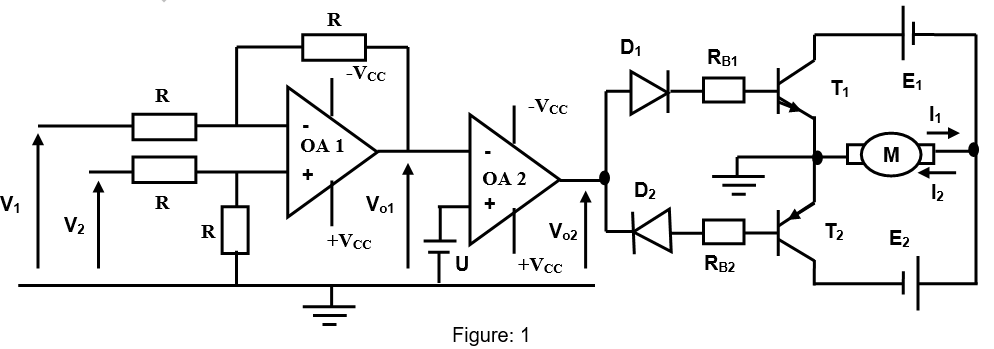
1. Control of a D.C
motor
|
|
a) Study of the control circuit (OA1; R’s and (AO2).
i) Give the operating mode of the operational amplifiers (OA1; R’s) and (AO2). (6 marks)
ii)
V- = (V1 + V01) / 2 (6 marks)
iii) Prove that the expression of the voltage at the OA1non- inverting input terminal in function of V2
V+ = (V2) / 2
iv) Express the voltage at the OA1 output terminal (V01) in function of V1 and V2
(6 marks)
v) What is the expression or the value of V02 when V01
> U, and when V01 < U (6 marks)
b) Study of the power circuit or motor circuit
i) When V02 > 0; what is the state [conduct (1) or block (0)] of the following elements D1, D2, T1, T2 and the motor? (5 marks)
ii) When V02 < 0; what is the state [conduct (1) or block (0)] of the following elements D1, D2, T1, T2 and the motor? (5 marks)
Section B: Optional
2. Uncontrolled half wave three-phase rectification
The circuit diagram of figure 2 represents a circuit of a three phase rectification supplying a purely resistive load R. The diodes are supposed to be perfect.
The expressions of the three phase
supply voltages are as follow:
|
Intervals |
D1 |
D2 |
D3 |
VL |
VD1 |
|
0 ≤ θ ≤ π/6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
π/6 ≤ θ ≤
5π/6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
5π/6 ≤ θ ≤
9π/6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
9π/6 ≤ θ ≤
12π/6 |
|
|
|
|
|
Table 1
a) Analyses the circuit of figure 2 above by drawing and completing the table 1 (10 marks)
b) Draw in bold on the same reference, the wave forms of the voltages V1, V2, V3, VL across the load R and VD1 across the diode D1 using appendix 1 (8marks)
c) Determine the maximum reverse voltage across D1. (3 marks)
d) Determine the duration of conduction for each diodes in terms of T. (3 marks)
e) Prove that
the average value of the voltage across the load is
__________________________________________________________________________________________
3. AC-AC
converter
The circuit of figure 3 below is that of an AC-AC converter. The supply voltage V(t) = 220√2sin100πt; its period is T and R is the resistance of the oven which have the value of 100Ω. T1 is fired at t0 and T2 at T/2 + t0.
4. Battery charger
It
is envisaged to design a battery charger for a mobile telephone; the
characteristics of the telephone and the battery are respectively 70mW and
300mAh; 3.6V; 0.11Ω. The device chosen for the conception of the charger is
shown in figure 4 below.
Assuming that all the components are
ideal; V1(t) = 220√ 2sin
wt; f = 50Hz; the transformation ratio of the transformer is 0.0205.
a) Give the significance of the following indications:
300mAh; 3.6V; 0.11Ω on the battery and 70mW on the telephone. (3 marks)
b) Draw the wave forms of the following voltages and
current V1(t); V2(t); VL(t) and IL(t) (4 marks)
c) Compute the value of the resistance R to be connected
in series with battery to reduce the maximum current in the load to
18.5mA. (4 marks)
d) Determine the turn-on and turn-off time of a diode.
Deduce the conduction period (4
marks)
e) Calculate the average value of the current in the
load. (4 marks)
f) Compute the charging time of the battery; express the answer in days, hours, minutes and seconds. (4 marks)
g) Calculate the effective load current (IL)
and the joule losses (4
marks)
IL = ILmas √ [ (tclosing
– topening)/T ]
h) Compute the useful power and efficiency of the set up (3 marks)
____________________________________________________________________________________
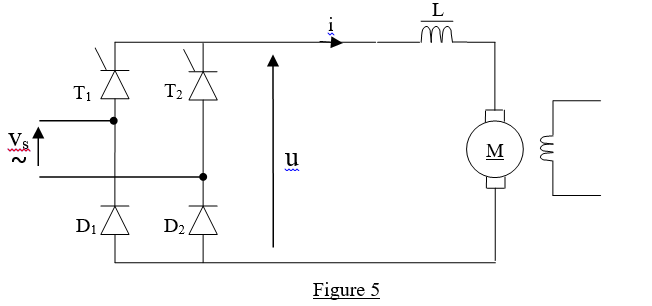
5. Mixed bridge rectification
Consider the half-controlled single phase bridge rectifier of figure 5. Thyristors and diodes are perfects
The inductance L of internal resistance 0.1Ω is large enough to cause constant current I = 25A flowing through the motor. The bridge delivers an average voltage U = 169V under a firing angle of 45°. The motor speed is 1800 rev/min.
a) Sketch the
waveform of Vs(t) and U(t), indicate the interval of conduction of each
component if Vs(t) is a sine waveform of 50Hz frequency (5 marks)
b) Calculate the effective value of Vs (5 marks)
c) Calculate the motor’s emf if the armature resistance
is 0.4Ω. (4 marks)
d) What is the mechanical power developed in the
armature? (4 marks)
e) Calculate the armature input power (4 marks)
f) What is the new value of emf if the mechanical torque
is doubled? (4 marks)
g) Deduce the new motor’ speed and comment (4 marks)